Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
A block of mass $M$ rests on a frictionless horizontal surface. It is connected to a fixed spring of constant $k$. A string attached to this block passes over a frictionless, massless pulley and is connected to a hanging block of mass $2M$. The system is released from rest with the spring in its relaxed (equilibrium) position.
- Find the combined kinetic energy of the two blocks when the hanging block has fallen a distance $d$.
- Find the kinetic energy of the hanging block at that same distance $d$.
- Find the maximum distance $d_{max}$ the hanging block falls before momentarily stopping.
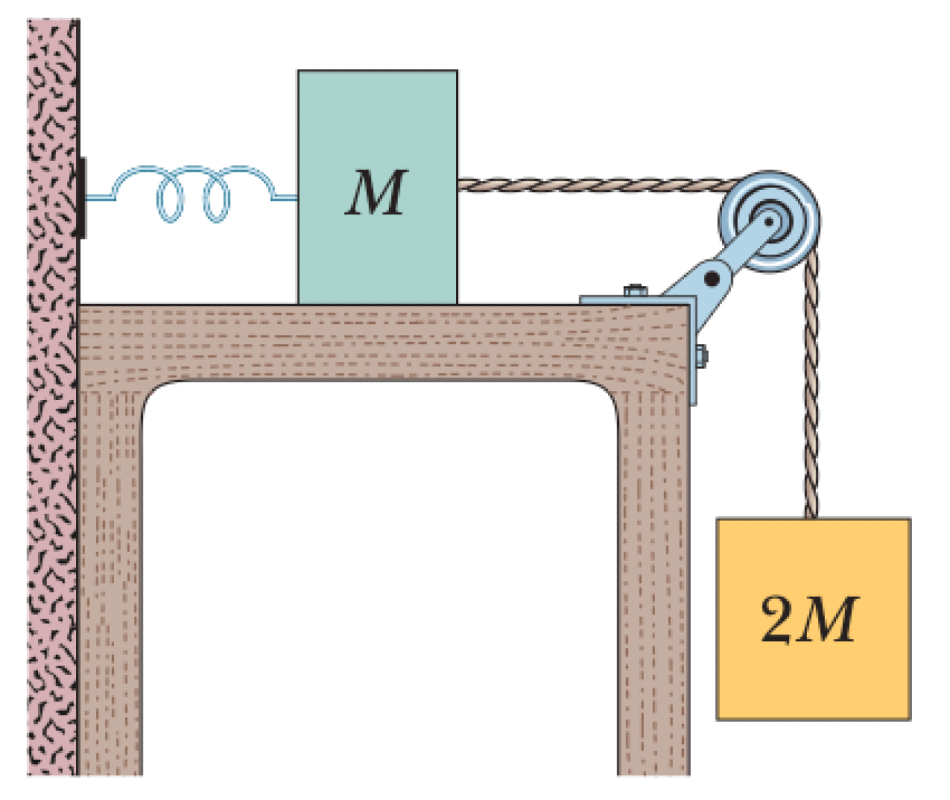
P0563-problem-1
[Q1] $K_{total} = 2Mgd - \frac{1}{2}kd^2$ [Q2] $K_{2M} = \frac{2}{3} \left( 2Mgd - \frac{1}{2}kd^2 \right)$ [Q3] $d_{max} = \frac{4Mg}{k}$
We apply the principle of conservation of mechanical energy to the system, which includes both blocks, the spring, and the Earth. Let the initial state be when the system is at rest, and the final state be when the hanging block has fallen a distance $y$. The initial position of the hanging block is our zero reference for gravitational potential energy ($U_g = 0$), and the spring is initially relaxed ($U_s = 0$).
The initial total energy is zero since the system starts from rest.
$$E_i = K_i + U_{g,i} + U_{s,i} = 0$$When the hanging block has fallen a distance $y$, the block on the table has moved the same distance $y$, stretching the spring. Both blocks move with the same speed $v$. The total kinetic energy is $K_{total} = \frac{1}{2}Mv^2 + \frac{1}{2}(2M)v^2 = \frac{3}{2}Mv^2$. The gravitational potential energy is $U_g = -(2M)gy$. The spring potential energy is $U_s = \frac{1}{2}ky^2$. The final total energy is $E_f = K_{total} - 2Mgy + \frac{1}{2}ky^2$.
By conservation of energy, $E_i = E_f$:
$$0 = K_{total} - 2Mgy + \frac{1}{2}ky^2$$[Q1] For a fallen distance $y=d$, the combined kinetic energy is:
$$K_{total} = 2Mgd - \frac{1}{2}kd^2$$[Q2] The kinetic energies of the blocks are $K_M = \frac{1}{2}Mv^2$ and $K_{2M} = \frac{1}{2}(2M)v^2$. The ratio is $K_{2M}/K_M = 2$. The kinetic energy of the hanging block is a fraction of the total:
$$K_{2M} = \frac{K_{2M}}{K_M + K_{2M}} K_{total} = \frac{2M}{M + 2M} K_{total} = \frac{2}{3} K_{total}$$[Q3] The hanging block reaches its maximum distance $d_{max}$ when its speed (and thus the system's kinetic energy) is momentarily zero. Setting $K_{total} = 0$ and $y = d_{max}$ in the energy conservation equation:
$$0 = 0 - 2Mgd_{max} + \frac{1}{2}kd_{max}^2$$Solving for the non-zero solution $d_{max}$:
$$d_{max} = \frac{4Mg}{k}$$