Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
A block of mass $m$ is pushed against a horizontal spring of spring constant $k$, compressing it by a distance $x$. The block is initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The block is then released and slides away from the spring. It leaves the spring at the spring's relaxed length and then travels over a rough horizontal floor with a coefficient of kinetic friction $\mu_k$. The block comes to a stop after traveling a distance $D$ on the rough surface.
- Find the increase in the thermal energy of the block-floor system, $\Delta E_{th}$.
- Find the maximum kinetic energy of the block, $K_{max}$.
- Find the original compression distance of the spring, $x$.
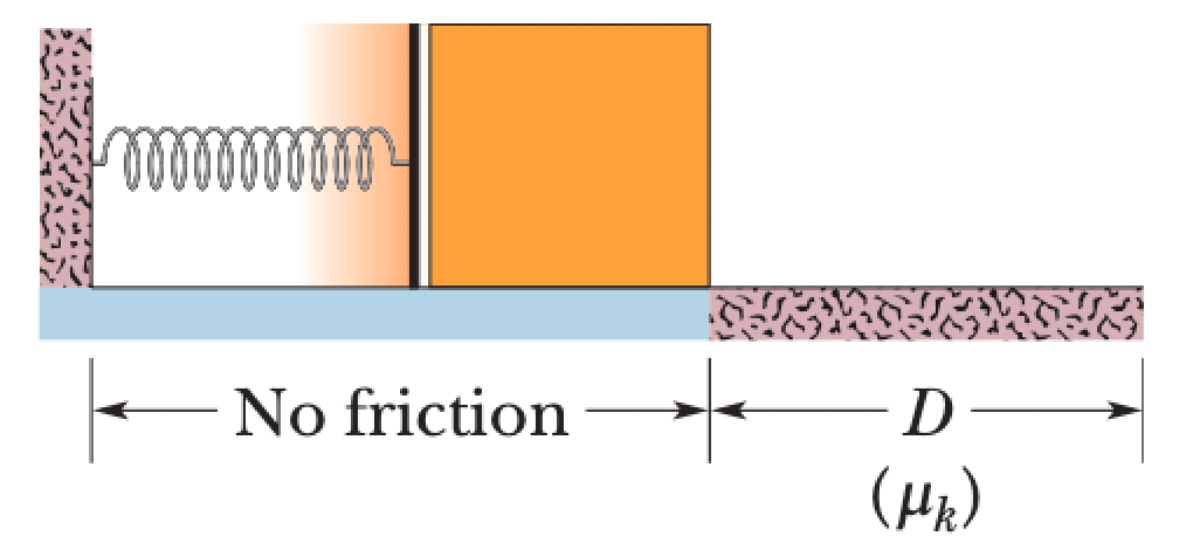
P0557-problem-1
[Q1] $\Delta E_{th} = \mu_k mgD$ [Q2] $K_{max} = \mu_k mgD$ [Q3] $x = \sqrt{\frac{2\mu_k mgD}{k}}$
Let the initial state be the block at rest against the compressed spring, and the final state be the block at rest after traveling distance $D$ on the rough surface. The maximum kinetic energy $K_{max}$ occurs at the point where the block leaves the spring (at its relaxed length).
[Q1] The increase in thermal energy is equal to the magnitude of the work done by the friction force, $f_k$. The friction force is $f_k = \mu_k N = \mu_k mg$, since the normal force $N$ equals the gravitational force $mg$. The work done by friction is $W_f = -f_k D$.
$$ \Delta E_{th} = -W_f = f_k D = \mu_k mgD $$[Q2] The block's kinetic energy is maximum just as it leaves the spring and enters the frictional region. This kinetic energy is then entirely dissipated by the work done by friction over the distance $D$. By the work-energy theorem on the rough surface:
$$ W_{net} = \Delta K $$ $$ -f_k D = K_{final} - K_{initial} = 0 - K_{max} $$ $$ K_{max} = f_k D = \mu_k mgD $$[Q3] We apply the law of conservation of energy to the entire process. The initial energy is the potential energy stored in the compressed spring, $U_s$. This energy is completely converted into thermal energy by the end.
$$ E_{initial} = E_{final} + \Delta E_{th} $$ $$ U_s = 0 + \Delta E_{th} $$ $$ \frac{1}{2}kx^2 = \mu_k mgD $$Solving for the compression distance $x$:
$$ x = \sqrt{\frac{2\mu_k mgD}{k}} $$