Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
A block of mass $m$ on a frictionless incline of angle $\theta$ is connected by a cord that runs over a massless, frictionless pulley to a light spring of spring constant $k$. The block is released from rest when the spring is unstretched.
- What is the speed $v$ of the block after it has moved a distance $d_1$ down the incline?
- How far $d_{max}$ down the incline does the block slide before momentarily stopping?
- What are the magnitude and direction of the block's acceleration at the instant it momentarily stops?
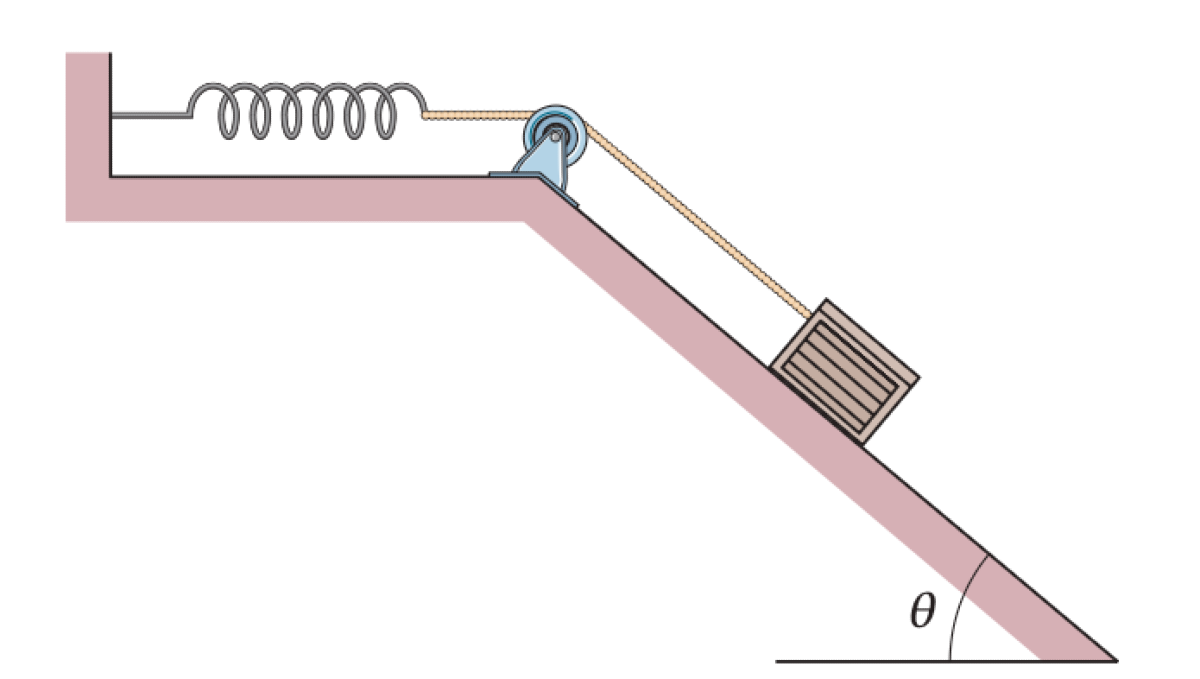
P0551-problem-1
[A1] $v = \sqrt{d_1\left(2g\sin\theta - \frac{kd_1}{m}\right)}$ [A2] $d_{max} = \frac{2mg\sin\theta}{k}$ [A3] Magnitude: $a = g\sin\theta$, Direction: Up the incline.
Let the system be the block, spring, and Earth. We apply the principle of conservation of mechanical energy. Let the initial position of the block be the reference height for gravitational potential energy ($U_g = 0$). The initial kinetic energy ($K_i$) and initial spring potential energy ($U_{s,i}$) are both zero.
When the block has moved a distance $x$ down the incline, its vertical position has changed by $-x\sin\theta$. The total mechanical energy $E$ is:
$$ E = K + U_g + U_s = \frac{1}{2}mv^2 - mgx\sin\theta + \frac{1}{2}kx^2 $$By conservation of energy, $E = E_i = 0$.
$$ \frac{1}{2}mv^2 - mgx\sin\theta + \frac{1}{2}kx^2 = 0 $$[Q1] To find the speed $v$ at a distance $x = d_1$:
$$ \frac{1}{2}mv^2 = mgd_1\sin\theta - \frac{1}{2}kd_1^2 $$ $$ v = \sqrt{2gd_1\sin\theta - \frac{k}{m}d_1^2} $$[Q2] The block stops momentarily when $v=0$ at $x=d_{max}$:
$$ -mgd_{max}\sin\theta + \frac{1}{2}kd_{max}^2 = 0 $$Since $d_{max} e 0$, we can divide by $d_{max}$:
$$ -mg\sin\theta + \frac{1}{2}kd_{max} = 0 \implies d_{max} = \frac{2mg\sin\theta}{k} $$[Q3] At the point of maximum displacement $d_{max}$, we use Newton's second law. Let the direction down the incline be positive. The forces along the incline are the component of gravity ($mg\sin\theta$) and the spring force ($F_s = -kd_{max}$).
$$ \sum F_x = mg\sin\theta - kd_{max} = ma $$Substitute the expression for $d_{max}$:
$$ ma = mg\sin\theta - k\left(\frac{2mg\sin\theta}{k}\right) = mg\sin\theta - 2mg\sin\theta = -mg\sin\theta $$ $$ a = -g\sin\theta $$The magnitude of the acceleration is $g\sin\theta$, and the negative sign indicates the direction is up the incline.