Source: Principles of Physics
Problem Sets:
Problem
A block is released from rest at a height $d=40$ cm. It slides down a frictionless ramp onto a first plateau of length $d$ with a coefficient of kinetic friction $\mu_k = 0.50$. If still moving, it descends a second frictionless ramp through a height $d/2$ and travels across a second plateau of length $d/2$, where the coefficient of kinetic friction is also $0.50$. Finally, if the block is still in motion, it moves up a frictionless ramp until it momentarily stops.
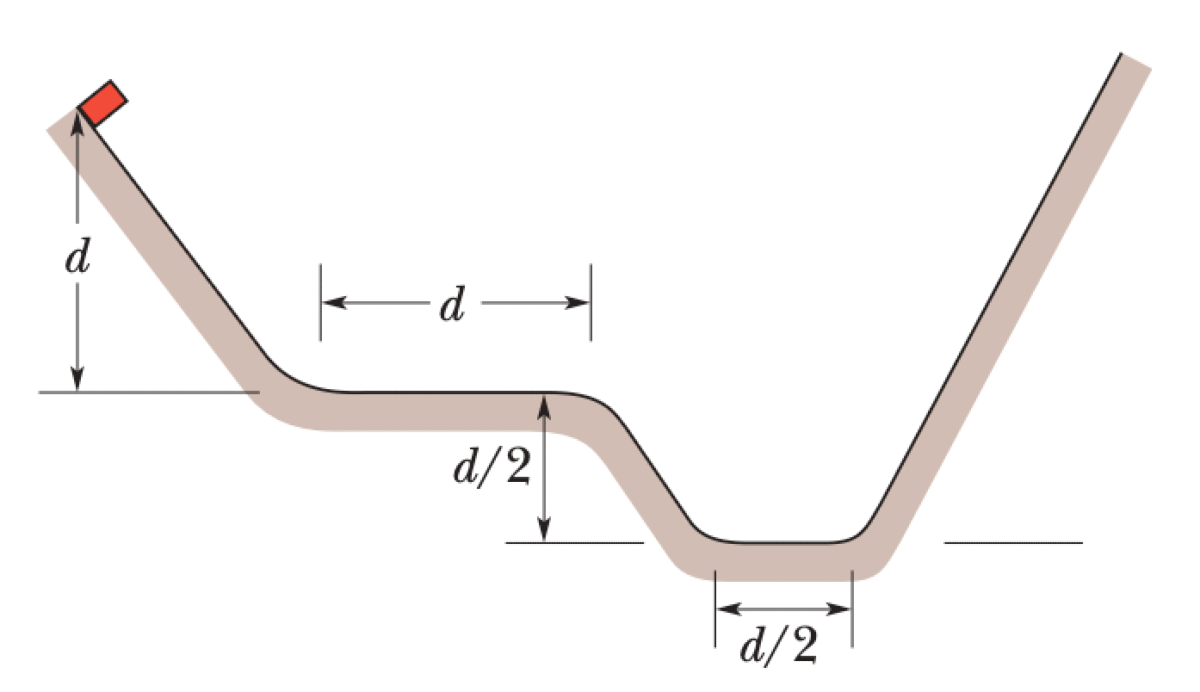
P0536-problem-1
H = 0.30 m
The total mechanical energy of the block-Earth system changes due to the work done by friction. We use the work-energy theorem, setting the gravitational potential energy reference ($U=0$) at the level of the lower plateau.
The block starts from rest at an initial height of $d + d/2$ above the reference level. The initial mechanical energy is entirely potential:
$$E_i = mg\left(d + \frac{d}{2}\right) = \frac{3}{2}mgd$$As the block traverses the two plateaus, friction does negative work, dissipating energy. Work done by friction on the first plateau: $W_{f1} = -f_k d = -\mu_k mgd$. Work done by friction on the second plateau: $W_{f2} = -f_k \frac{d}{2} = -\frac{1}{2}\mu_k mgd$. The total work done by non-conservative forces is $W_{nc} = W_{f1} + W_{f2} = -\frac{3}{2}\mu_k mgd$.
The block's final state is momentarily at rest ($K_f = 0$) at a height $H$ on the last ramp. The final mechanical energy is:
$$E_f = mgH$$Applying the work-energy theorem, $\Delta E = E_f - E_i = W_{nc}$:
$$mgH - \frac{3}{2}mgd = -\frac{3}{2}\mu_k mgd$$ $$mgH = \frac{3}{2}mgd - \frac{3}{2}\mu_k mgd = \frac{3}{2}mgd(1 - \mu_k)$$ $$H = \frac{3}{2}d(1 - \mu_k)$$Substituting the given values:
$$H = \frac{3}{2}(0.40 \text{ m})(1 - 0.50) = \frac{3}{2}(0.40 \text{ m})(0.50) = 0.30 \text{ m}$$Since $H>0$, the block does not stop on either plateau and reaches the final ramp.