Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
As a particle moves along an x axis, a force in the positive direction of the axis acts on it. The provided figure shows the magnitude $F$ of the force versus position $x$ of the particle. The curve is given by $F = a/x^2$, with $a = 9.0 \text{ N} \cdot \text{m}^2$.
- Find the work done on the particle by the force as the particle moves from $x = 1.0 \text{ m}$ to $x = 3.0 \text{ m}$ by estimating the work from the graph.
- Find the work done on the particle by the force as the particle moves from $x = 1.0 \text{ m}$ to $x = 3.0 \text{ m}$ by integrating the force function.
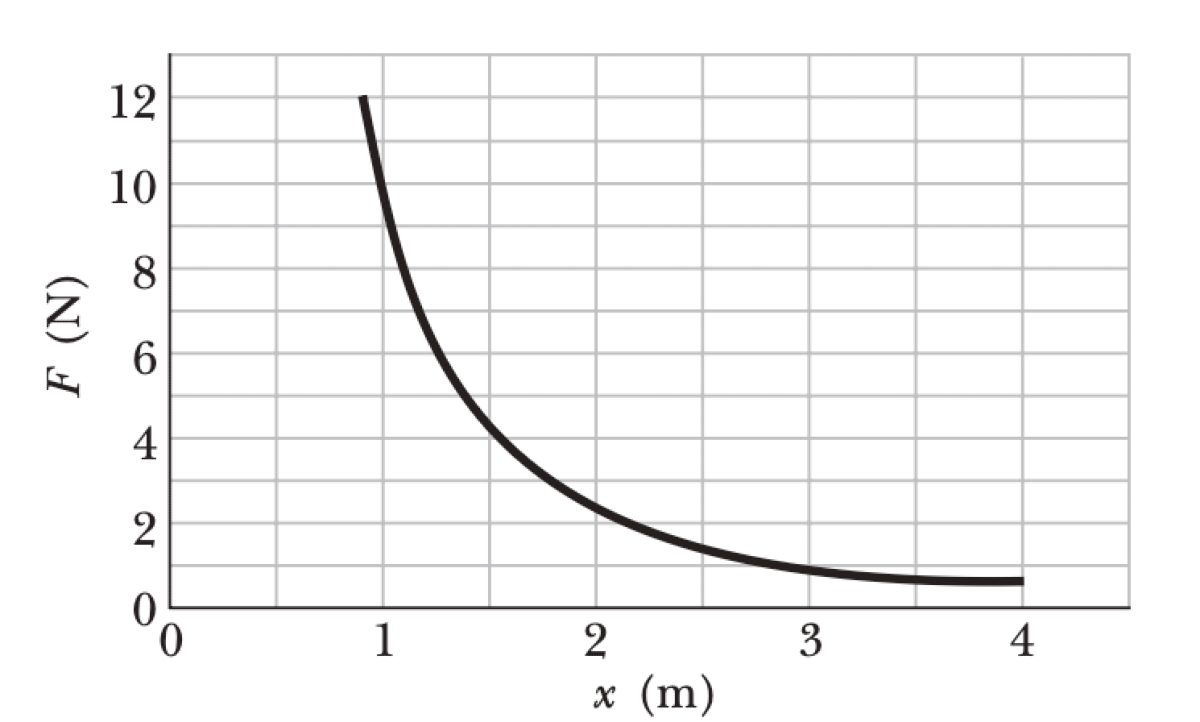
P0525-problem-1
[Q1] $W \approx 6.0 \text{ J}$ [Q2] $W = 6.0 \text{ J}$
[Q1] The work done is the area under the force-position ($F-x$) curve. We can estimate this area by counting the grid boxes between $x=1.0 \text{ m}$ and $x=3.0 \text{ m}$. Each box on the graph has a width of $0.5 \text{ m}$ and a height of $2 \text{ N}$, so the area of one box represents a work of $(0.5 \text{ m})(2 \text{ N}) = 1 \text{ J}$. There are approximately 6 boxes under the curve in the specified interval.
$$W \approx (\text{number of boxes}) \times (\text{work per box})$$ $$W \approx (6)(1 \text{ J}) = 6.0 \text{ J}$$[Q2] The work done by a variable force $F(x)$ along the x-axis from an initial position $x_i$ to a final position $x_f$ is given by the integral:
$$W = \int_{x_i}^{x_f} F(x) \,dx$$Substituting the given force function $F(x) = a/x^2$ and the limits of integration $x_i=1.0 \text{ m}$ and $x_f=3.0 \text{ m}$:
$$W = \int_{1.0}^{3.0} \frac{a}{x^2} dx = a \int_{1.0}^{3.0} x^{-2} dx$$ $$W = a \left[ -\frac{1}{x} \right]_{1.0}^{3.0} = a \left( -\frac{1}{3.0} - (-\frac{1}{1.0}) \right) = a \left( 1 - \frac{1}{3} \right) = \frac{2a}{3}$$Substituting $a = 9.0 \text{ N} \cdot \text{m}^2$:
$$W = \frac{2(9.0 \text{ N} \cdot \text{m}^2)}{3} = 6.0 \text{ J}$$