Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
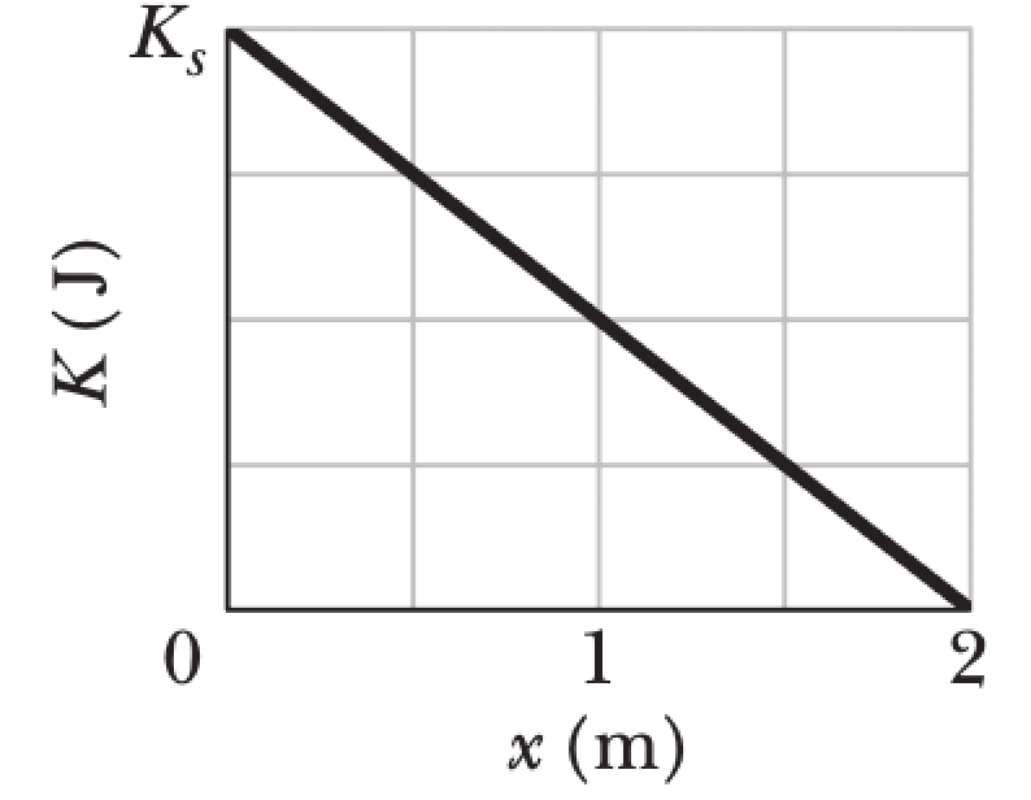
A block is sent up a frictionless ramp along which an x axis extends upward. Figure below gives the kinetic energy of the block as a function of position x; the scale of the figure's vertical axis is set by $K_s = 40.0$ J. If the block's initial speed is 4.00 m/s, what is the normal force on the block?
P0518-problem-1
[Q1] N = 44.7 N
The mass of the block can be found from its initial kinetic energy, $K_i = K_s$, and initial speed, $v_i$.
$$K_i = \frac{1}{2}mv_i^2 \implies m = \frac{2K_i}{v_i^2}$$According to the work-energy theorem, the change in kinetic energy equals the net work done on the block. The only force doing work is the component of gravity parallel to the ramp, $F_{gx} = mg\sin\theta$.
$$\Delta K = W_{net} = -F_{gx} \Delta x$$From the graph, $\Delta K = K_f - K_i = 0 - K_s = -K_s$ over a distance $\Delta x = 2.0$ m.
$$-K_s = -F_{gx} \Delta x \implies F_{gx} = \frac{K_s}{\Delta x}$$The magnitude of the gravitational force is $F_g = mg$. The normal force, $N$, is the component of gravity perpendicular to the ramp, $F_{gy} = mg\cos\theta$. These components are related by $F_g^2 = F_{gx}^2 + F_{gy}^2$. Since $N=F_{gy}$, we can find the normal force.
$$N = \sqrt{F_g^2 - F_{gx}^2} = \sqrt{(mg)^2 - \left(\frac{K_s}{\Delta x}\right)^2}$$First, calculate the mass:
$$m = \frac{2(40.0 \text{ J})}{(4.00 \text{ m/s})^2} = 5.00 \text{ kg}$$Next, calculate the forces:
$$F_g = mg = (5.00 \text{ kg})(9.8 \text{ m/s}^2) = 49.0 \text{ N}$$ $$F_{gx} = \frac{40.0 \text{ J}}{2.0 \text{ m}} = 20.0 \text{ N}$$Finally, calculate the normal force:
$$N = \sqrt{(49.0 \text{ N})^2 - (20.0 \text{ N})^2}$$