Source: High school physics (Chinese)
Problem Sets:
Problem
As shown in Figure below, a small block slides down an incline from point A and finally stops at point B on a horizontal plane. It is known that point A is at a height H above point B, and the horizontal distance between A and B is s. The incline and the horizontal plane are made of the same material.
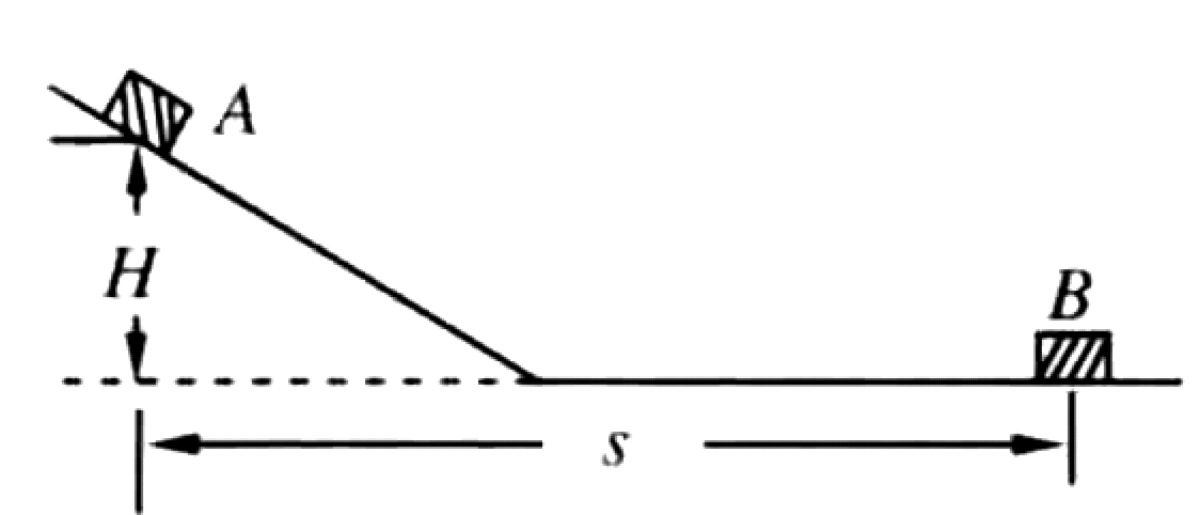
P0469-problem-1
The relation $\mu = H/s$ is proven.
Apply the work-energy theorem from the start at A to the end at B. The initial and final kinetic energies are zero, so the net work done on the block is zero.
$$W_{net} = \Delta K = 0$$The net work is the sum of the work done by gravity ($W_g$) and the work done by friction ($W_f$). Work by gravity: $W_g = mgH$. The work done by friction is $W_f = -\mu \int N \, dl$. The friction force $f = \mu N$ always opposes the displacement. Let the horizontal projection of the incline be $s_1$ and the length of the horizontal path be $s_2$, so $s = s_1 + s_2$. On the incline, the normal force is $N_1 = mg\cos\theta$ and the distance is $d_1 = s_1/\cos\theta$. The work done by friction is $W_{f1} = -f_1 d_1 = -(\mu mg\cos\theta)(s_1/\cos\theta) = -\mu mgs_1$. On the horizontal plane, the normal force is $N_2 = mg$. The work done by friction is $W_{f2} = -f_2 s_2 = -\mu mgs_2$. Total work by friction: $W_f = W_{f1} + W_{f2} = -\mu mgs_1 - \mu mgs_2 = -\mu mg(s_1 + s_2) = -\mu mgs$. Setting the net work to zero:
$$W_g + W_f = 0$$ $$mgH - \mu mgs = 0$$ $$mgH = \mu mgs$$ $$\mu = \frac{H}{s}$$