Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
Block B, of weight $W_B$, rests on a horizontal table. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the table is $\mu_s$. A system of cords connects block B, a hanging block A of weight $W_A$, and a wall, with one cord making an angle $\theta$ with the horizontal. The system is in static equilibrium.
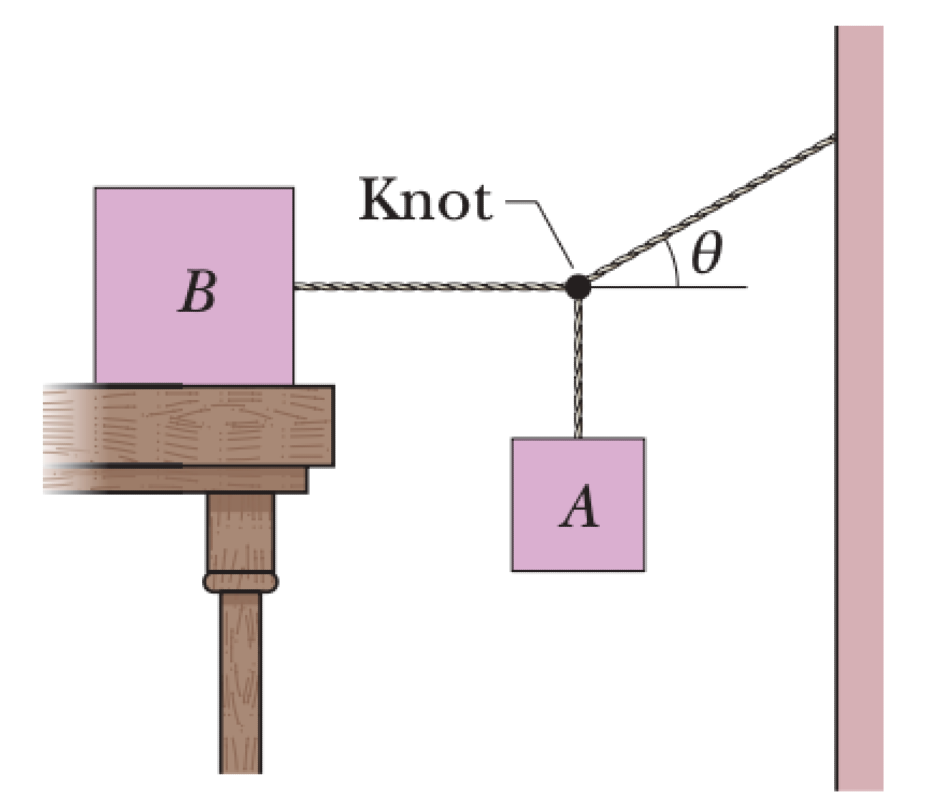
01K63JQ1PJ2XQ339RKMK2BBY3Q
For the system to be in static equilibrium, the net force on the knot must be zero. Let $T_B$ be the tension in the horizontal cord, and $T_{wall}$ be the tension in the angled cord.
Summing forces on the knot:
$$ \sum F_y = T_{wall} \sin\theta - W_A = 0 \implies W_A = T_{wall} \sin\theta $$ $$ \sum F_x = T_{wall} \cos\theta - T_B = 0 \implies T_B = T_{wall} \cos\theta $$Dividing the vertical component equation by the horizontal one yields a direct relationship between $W_A$ and $T_B$:
$$ \frac{W_A}{T_B} = \frac{T_{wall} \sin\theta}{T_{wall} \cos\theta} = \tan\theta \implies W_A = T_B \tan\theta $$For the maximum weight $W_{A,max}$, block B must be on the verge of sliding. At this point, the tension $T_B$ equals the maximum static friction force, $f_{s,max}$. The forces on block B are in equilibrium. The normal force $N$ from the table equals the block's weight, $N = W_B$. The maximum static friction is $f_{s,max} = \mu_s N = \mu_s W_B$. Therefore, the maximum horizontal tension is $T_{B,max} = \mu_s W_B$.
Substituting this maximum tension into the equation for the knot gives the maximum weight of block A:
$$ W_{A,max} = T_{B,max} \tan\theta $$ $$ W_{A,max} = \mu_s W_B \tan\theta $$