Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
Three blocks with masses $m_1$, $m_2$, and $m_3$ are connected by ropes and pulleys as shown. Block 2 rests on a horizontal table. Assume the ropes and pulleys are massless and frictionless, and that $m_3 > m_1$. When the system is released from rest, it accelerates with a magnitude $a$.
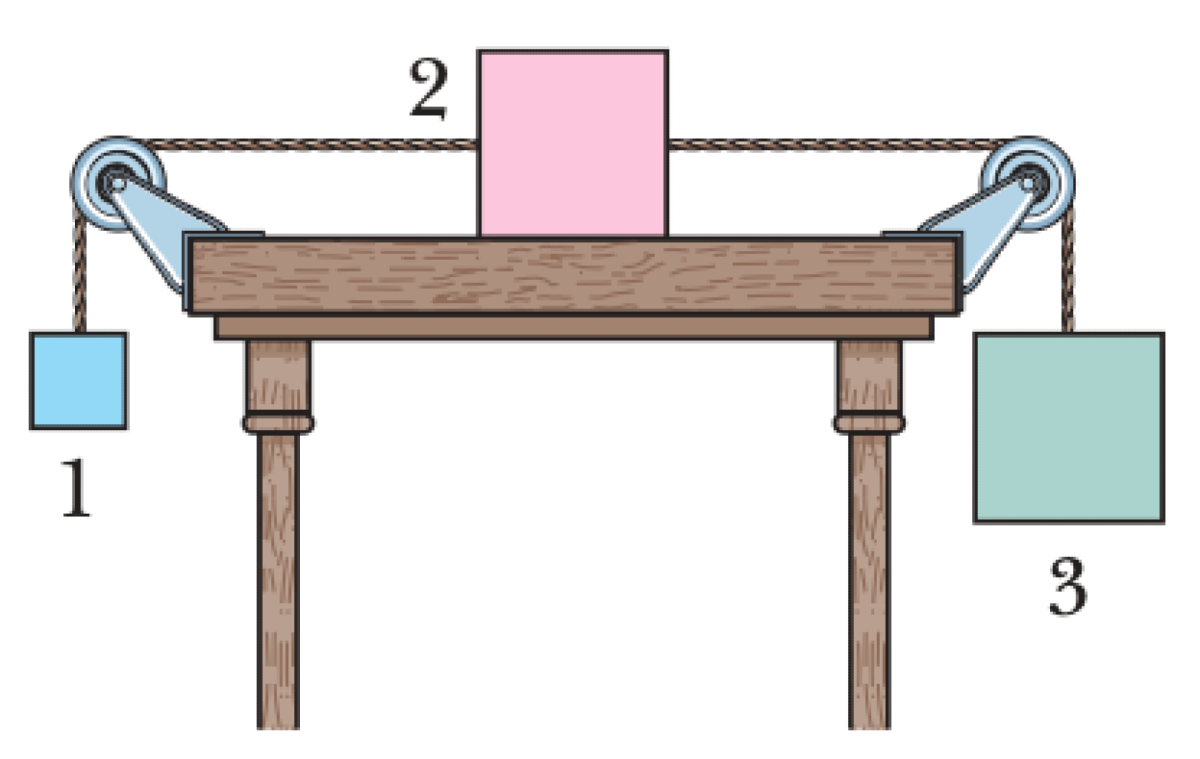
01K63JMQCTZTJ0D90GXMJHT7HE
We analyze the three blocks as a single system. The total mass is $M_{tot} = m_1 + m_2 + m_3$.
Assuming $m_3 > m_1$, the net force driving the motion is the difference in weights of the hanging blocks, opposed by the kinetic friction on block 2. Applying Newton's second law, $F_{net} = M_{tot}a$:
$$m_3g - m_1g - f_k = (m_1 + m_2 + m_3)a$$The kinetic friction force on block 2 is $f_k = \mu_k N$. Since block 2 is on a horizontal surface, the normal force $N$ equals its weight, $N = m_2g$.
$$f_k = \mu_k m_2 g$$Substitute the expression for $f_k$ into the system equation:
$$(m_3 - m_1)g - \mu_k m_2 g = (m_1 + m_2 + m_3)a$$Now, we algebraically solve for the coefficient of kinetic friction $\mu_k$:
$$\mu_k m_2 g = (m_3 - m_1)g - (m_1 + m_2 + m_3)a$$ $$\mu_k = \frac{(m_3 - m_1)g - (m_1 + m_2 + m_3)a}{m_2 g}$$