Source: Principles of Physics
Problem Sets:
Problem
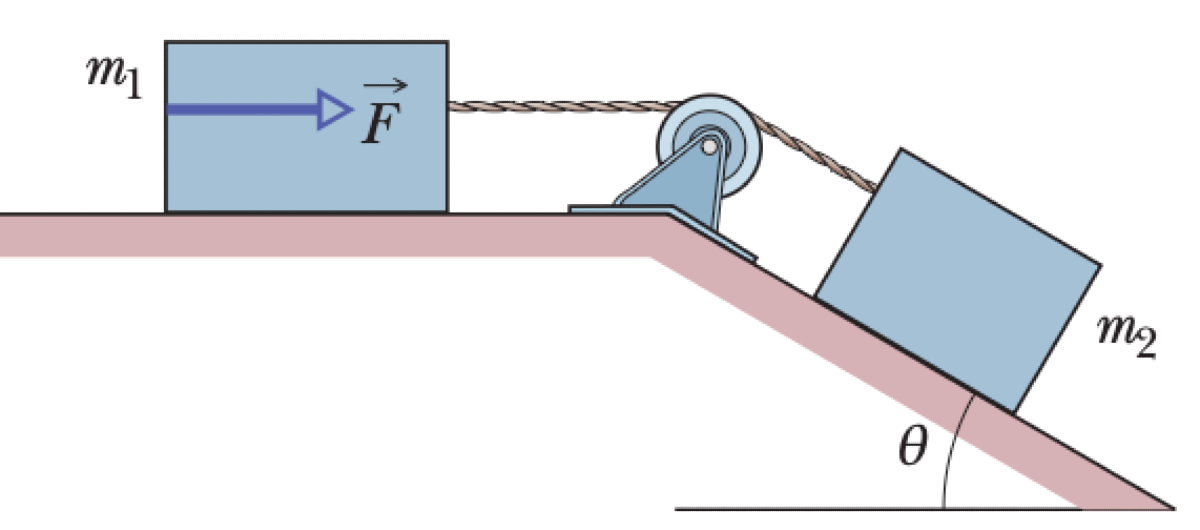
A block of mass $m_1$ on a horizontal frictionless surface is connected by a massless cord over a massless, frictionless pulley to a block of mass $m_2$ on a frictionless plane inclined at an angle $\theta$. A horizontal force $\vec{F}$ is applied to $m_1$.
- If the force $\vec{F}$ is directed to the left with magnitude $F$, what is the tension $T$ in the cord?
- If the force $\vec{F}$ is directed to the right, what is its largest magnitude, $F_{max}$, for which the cord remains taut?
01K629S6W4K6QEXST2NZHRWS9J
[Q1] $T = \frac{m_2(F + m_1 g \sin\theta)}{m_1 + m_2}$ [Q2] $F_{max} = m_1 g \sin\theta$
Let $a$ be the magnitude of the system's acceleration. All surfaces are frictionless.
[Q1] Assume the system accelerates with $m_1$ moving to the right and $m_2$ moving down the incline. The leftward force $F$ opposes this motion for $m_1$. Applying Newton's second law to each mass in the direction of motion:
$$T - F = m_1 a \quad \quad (1)$$ $$m_2 g \sin\theta - T = m_2 a \quad \quad (2)$$To find the tension $T$, we first eliminate the acceleration $a$. From (1), $a = (T-F)/m_1$. Substituting this into (2):
$$m_2 g \sin\theta - T = m_2 \left(\frac{T-F}{m_1}\right)$$Multiplying by $m_1$ and rearranging to solve for $T$:
$$m_1 m_2 g \sin\theta - m_1 T = m_2 T - m_2 F$$ $$m_1 m_2 g \sin\theta + m_2 F = T(m_1 + m_2)$$ $$T = \frac{m_2(m_1 g \sin\theta + F)}{m_1 + m_2}$$[Q2] The cord will become slack if block $m_1$ is pulled to the right with an acceleration that block $m_2$ cannot match. The limiting condition occurs when the acceleration of $m_1$ under the force $F_{max}$ (if the cord were cut) equals the natural free-fall acceleration of $m_2$ down the incline.
The unconstrained acceleration of $m_1$ due to a rightward force $F_{max}$ is:
$$a_1 = \frac{F_{max}}{m_1}$$The unconstrained acceleration of $m_2$ down the frictionless incline is:
$$a_2 = g \sin\theta$$Setting these accelerations equal gives the maximum force before the cord would become slack:
$$\frac{F_{max}}{m_1} = g \sin\theta$$ $$F_{max} = m_1 g \sin\theta$$