Source: High school physics (Chinese)
Problem Sets:
Problem
As shown in Figure, an object of mass $m$ is placed on an escalator. The object remains at rest relative to the escalator. The escalator moves upwards.
- When the escalator moves upwards at a constant velocity, what are the normal force and static friction force acting on the object?
- The escalator accelerates upwards with an acceleration of magnitude $a$. What are the normal force and static friction force acting on the object?
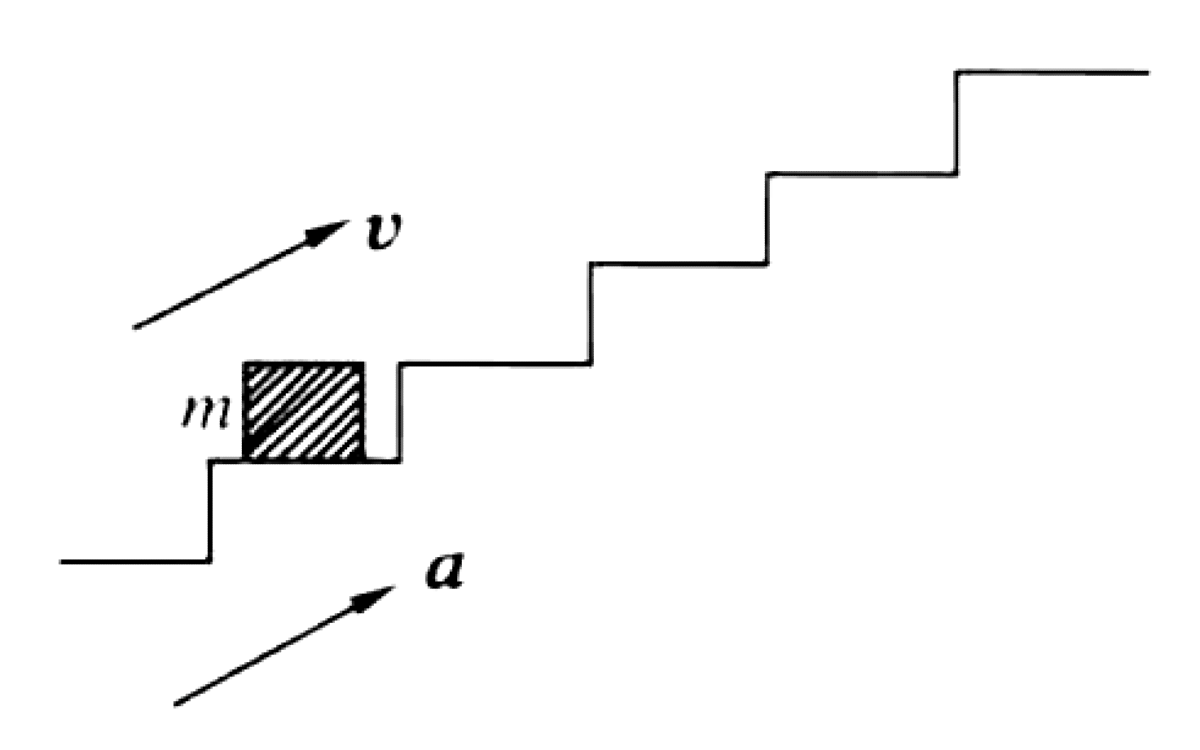
01K5YZWD69XCT93YQF931K1QYK
Let $\theta$ be the angle of inclination of the escalator.
[Q1] For constant velocity motion ($a=0$): The normal force is:
$$ N = mg $$The static friction force is:
$$ f_s = 0 $$[Q2] For upward acceleration of magnitude $a$: The normal force is:
$$ N = m(g + a\sin\theta) $$The static friction force is:
$$ f_s = ma\cos\theta $$We analyze the forces on the object in a stationary (inertial) frame of reference. Let the x-axis be horizontal and the y-axis be vertical. Let $\theta$ be the angle of inclination of the escalator with respect to the horizontal, as indicated by the direction of the velocity and acceleration vectors in the figure.
The forces acting on the object of mass $m$ are:
- Gravitational force, $\vec{F}_g$, with magnitude $mg$ acting vertically downwards.
- Normal force, $\vec{N}$, exerted by the horizontal surface of the step, acting vertically upwards.
- A horizontal force, $\vec{f}_s$, exerted by the vertical riser of the step, which the problem refers to as the static friction force.
The object remains at rest relative to the escalator, so its acceleration $\vec{a}$ is the same as that of the escalator. The components of this acceleration are:
$a_x = a \cos\theta$ $a_y = a \sin\theta$We apply Newton's Second Law, $\sum \vec{F} = m\vec{a}$, in component form. Sum of forces in the x-direction (horizontal):
$$ \sum F_x = f_s = ma_x $$ $$ f_s = ma\cos\theta $$Sum of forces in the y-direction (vertical):
$$ \sum F_y = N - mg = ma_y $$ $$ N - mg = ma\sin\theta $$Solving for the normal force $N$:
$$ N = mg + ma\sin\theta = m(g + a\sin\theta) $$These derived equations are the general expressions for the forces.
[Q1] When the escalator moves upwards at a constant velocity, what are the normal force and static friction force acting on the object?
For constant velocity motion, the acceleration is zero, $a=0$. We substitute this value into our general expressions. Normal force:
$$ N = m(g + (0)\sin\theta) = mg $$Static friction force:
$$ f_s = m(0)\cos\theta = 0 $$At constant velocity, the normal force equals the object's weight, and the static friction force is zero, as the net force must be zero.
[Q2] The escalator accelerates upwards with an acceleration of magnitude $a$. What are the normal force and static friction force acting on the object?
For this case, we use the general expressions derived above with the non-zero acceleration $a$. Normal force:
$$ N = m(g + a\sin\theta) $$Static friction force:
$$ f_s = ma\cos\theta $$The normal force is greater than the object's weight, and a horizontal static friction force is required to provide the horizontal component of the acceleration.