Source: Principles of Physics
Problem Sets:
Problem
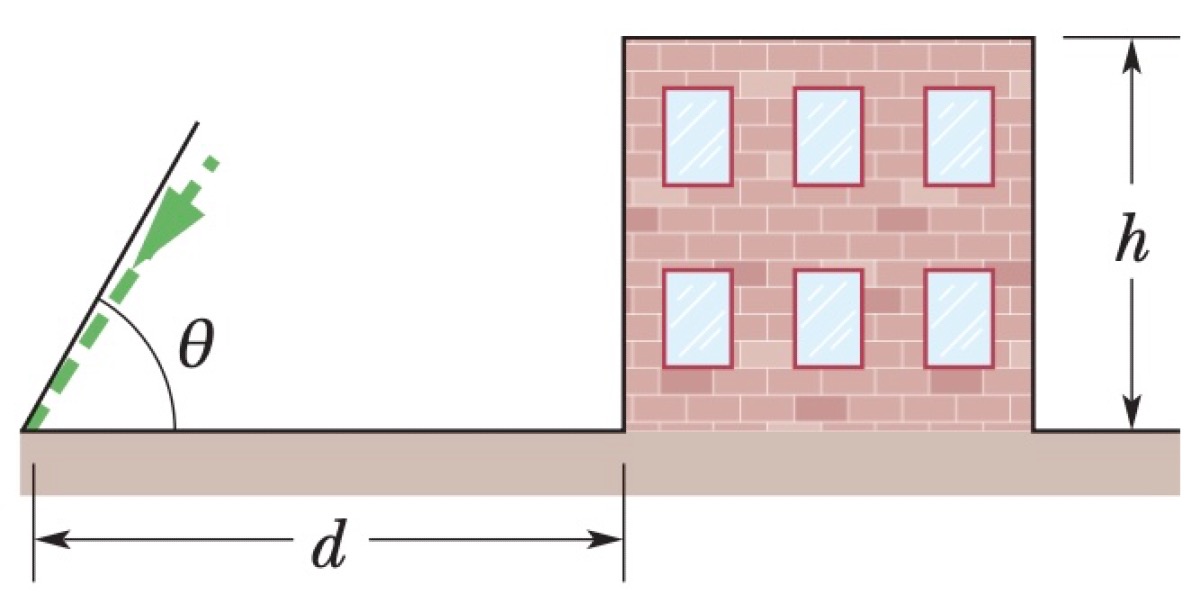
A ball is thrown from the edge of a roof at a height $h$ above the ground. The ball hits the ground after a time $t$ at a horizontal distance $d$ from the building, making an angle $\theta$ with the horizontal.
- Find the height $h$.
- Find the magnitude of the initial velocity, $v_0$.
- Find the angle $\phi_0$ of the initial velocity relative to the horizontal.
- Determine the condition for the initial velocity to be directed above or below the horizontal.
[Q1] $h = d\tan\theta - \frac{1}{2}gt^2$ [Q2] $v_0 = \sqrt{\left(\frac{d}{t}\right)^2 + \left(gt - \frac{d}{t}\tan\theta\right)^2}$ [Q3] $\phi_0 = \arctan\left(\left|\frac{gt^2}{d} - \tan\theta\right|\right)$ [Q4] The angle is above the horizontal if $gt^2 > d\tan\theta$ and below if $gt^2 < d\tan\theta$.
We analyze the motion by separating it into horizontal (x) and vertical (y) components. Let the origin be the launch point, with positive y upwards.
The horizontal velocity is constant since there is no horizontal acceleration.
$$|v_x| = \frac{d}{t}$$At impact, the final velocity components $v_{fx}$ and $v_{fy}$ are related by the angle $\theta$:
$$|v_{fy}| = |v_{fx}|\tan\theta = \frac{d}{t}\tan\theta$$The final vertical velocity is $v_{fy} = v_{y0} - gt$. Since the ball is moving downward at impact, $v_{fy}$ is negative. We can solve for the initial vertical velocity $v_{y0}$:
$$v_{y0} = v_{fy} + gt = -\frac{d}{t}\tan\theta + gt$$[Q1] The vertical displacement is $\Delta y = -h$. Using the kinematic equation:
$$-h = v_{y0}t - \frac{1}{2}gt^2$$Substituting the expression for $v_{y0}$:
$$-h = \left(gt - \frac{d}{t}\tan\theta\right)t - \frac{1}{2}gt^2 = gt^2 - d\tan\theta - \frac{1}{2}gt^2$$ $$h = d\tan\theta - \frac{1}{2}gt^2$$[Q2] The magnitude of the initial velocity $v_0$ is found from its components, $v_0 = \sqrt{v_x^2 + v_{y0}^2}$.
[Q3] The angle of the initial velocity $\phi_0$ relative to the horizontal is found using $\tan\phi_0 = |v_{y0}/v_x|$.
[Q4] The initial velocity is directed above the horizontal if $v_{y0} > 0$ and below if $v_{y0} < 0$. This depends on the sign of $gt - (d/t)\tan\theta$.