Source: Principles of Physics
Problem
A projectile is launched from ground level. A graph of its speed $v$ versus time $t$ shows an initial speed $v_0$ at $t=0$. The speed decreases to a minimum value $v_{min}$ at time $t_h$ and then increases.
- What is the total horizontal distance $R$ the projectile travels before returning to ground level?
- What is the maximum height $H$ attained by the projectile?

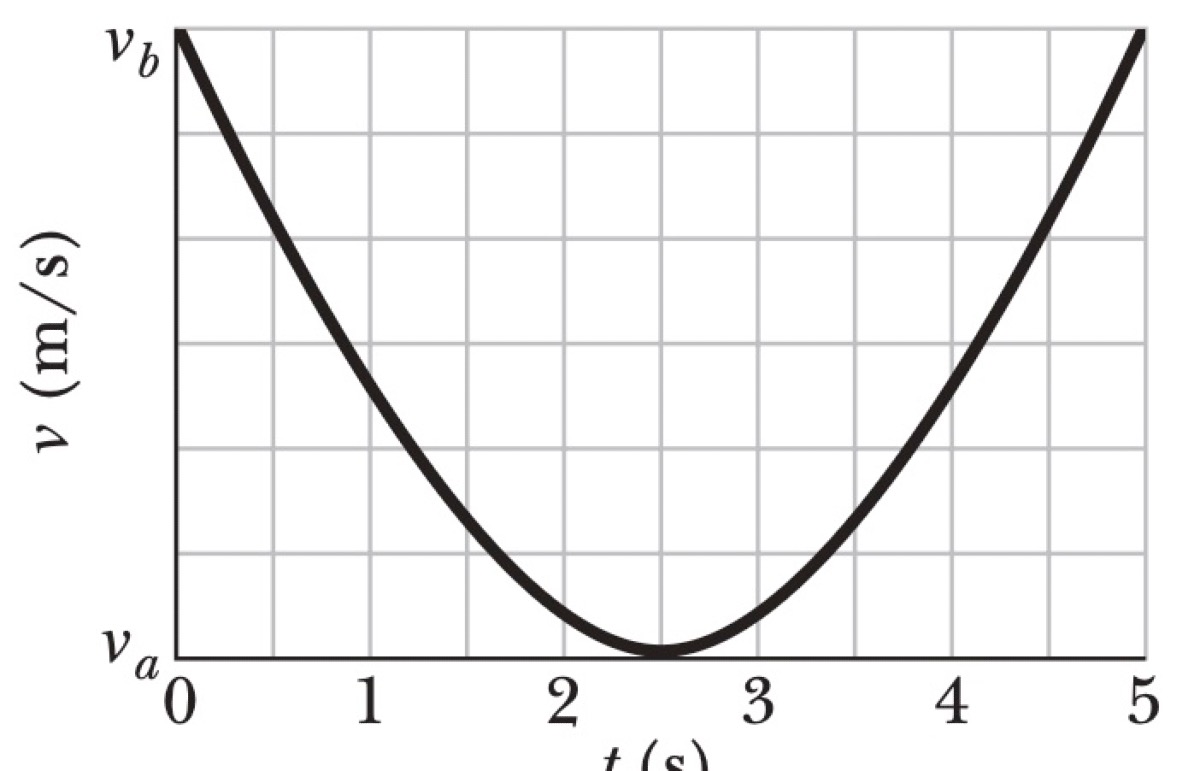
P0303-problem-2
[Q1] $R = 2v_{min}t_h$ [Q2] $H = \frac{1}{2}t_h\sqrt{v_0^2 - v_{min}^2}$
The speed of a projectile is $v = \sqrt{v_x^2 + v_y^2}$. The horizontal velocity $v_x$ is constant, while the vertical velocity $v_y$ changes due to gravity. The speed is minimum when $v_y = 0$, which occurs at the peak of the trajectory. Therefore, the minimum speed is the horizontal velocity:
$$v_x = v_{min}$$The time to reach this peak is given as $t_h$. For a symmetric trajectory starting and ending at ground level, the total time of flight is $T = 2t_h$.
The initial speed is $v_0$, which is composed of horizontal and vertical components: $v_0^2 = v_x^2 + v_{y0}^2$. We can find the initial vertical velocity $v_{y0}$:
$$v_{y0} = \sqrt{v_0^2 - v_x^2} = \sqrt{v_0^2 - v_{min}^2}$$[Q1] The horizontal range $R$ is the constant horizontal velocity multiplied by the total flight time:
$$R = v_x T = v_{min} (2t_h)$$[Q2] The maximum height $H$ is the vertical distance traveled in time $t_h$. Using the kinematic equation $H = \frac{v_{y0} + v_y}{2}t$, where $v_y = 0$ at the peak:
$$H = \frac{v_{y0} + 0}{2} t_h = \frac{1}{2}v_{y0}t_h$$Substituting the expression for $v_{y0}$:
$$H = \frac{1}{2}t_h\sqrt{v_0^2 - v_{min}^2}$$