Source: Principles of Physics
Problem Sets:
Problem
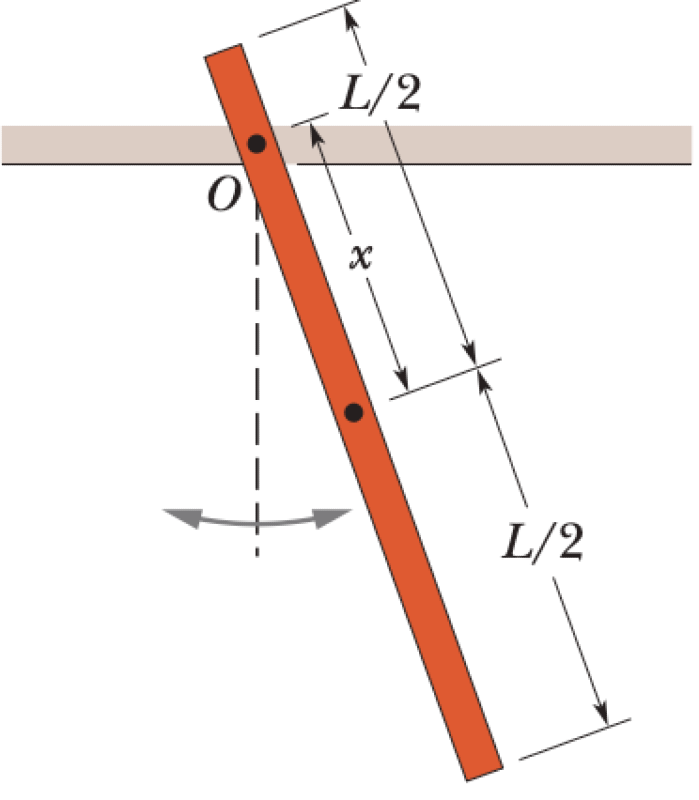
A stick of length L = 1.85 m oscillates as a physical pendulum. The pivot point O is a distance x from the stick's center of mass.
- What value of distance x gives the least period?
- What is that least period?
P0679-problem-1
[Q1] x = 0.534 m [Q2] T_min = 2.07 s
The period of a physical pendulum is $T = 2\pi \sqrt{I/(mgx)}$. By the parallel-axis theorem, the moment of inertia about the pivot O is $I = I_{com} + mx^2$. For a uniform stick, $I_{com} = \frac{1}{12}mL^2$.
$$T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{\frac{1}{12}mL^2 + mx^2}{mgx}} = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{\frac{L^2}{12x} + x}{g}}$$[Q1] To find the minimum period, we must minimize the term $f(x) = \frac{L^2}{12x} + x$. By the AM-GM inequality, this term is minimized when its two components are equal.
$$\frac{L^2}{12x} = x \implies x^2 = \frac{L^2}{12}$$ $$x = \frac{L}{\sqrt{12}} = \frac{1.85 \text{ m}}{\sqrt{12}} = 0.534 \text{ m}$$[Q2] The minimum period $T_{min}$ is found by substituting $x=L/\sqrt{12}$ into the period equation. The minimized term inside the square root becomes $(x+x)/g = 2x/g$.
$$T_{min} = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{2x}{g}} = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{2(L/\sqrt{12})}{g}} = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{L}{g\sqrt{3}}}$$ $$T_{min} = 2\pi\sqrt{\frac{1.85 \text{ m}}{(9.8 \text{ m/s}^2)\sqrt{3}}} = 2.07 \text{ s}$$