Source: Principles of Physics
Problem Sets:
Problem
Two springs are joined and connected to a block of mass $m$ that is set oscillating over a frictionless floor. The springs each have a spring constant $k$.
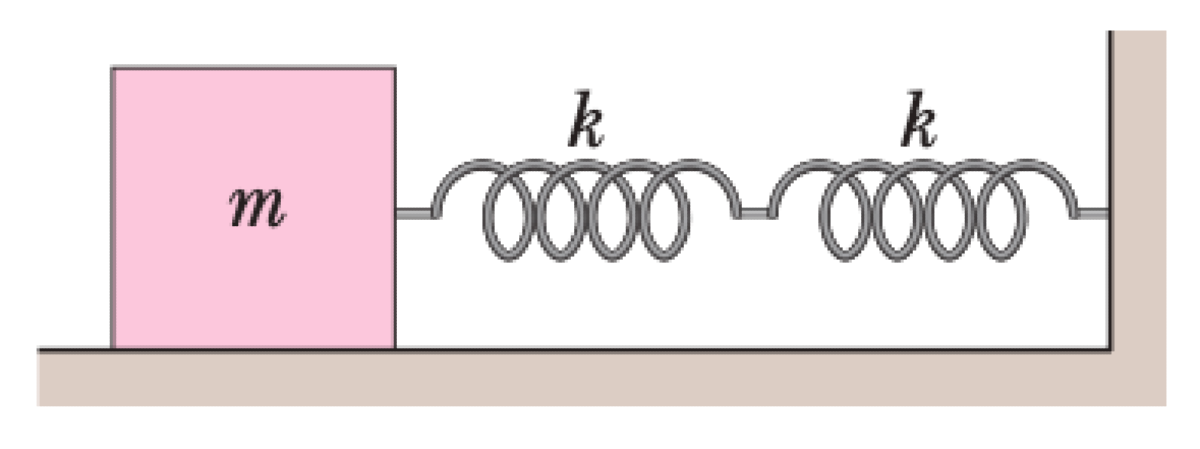
P0672-problem-1
The two springs are in series. The effective spring constant, $k_{eff}$, is found by considering the total extension for a given force $F$. The total extension $\Delta x$ is the sum of the individual extensions, $\Delta x = \Delta x_1 + \Delta x_2$. Since $F = k_1 \Delta x_1 = k_2 \Delta x_2$ and $k_1 = k_2 = k$, we have $\Delta x_1 = F/k$ and $\Delta x_2 = F/k$. The effective spring constant is defined by $F = k_{eff} \Delta x$.
$$F = k_{eff} (\Delta x_1 + \Delta x_2) = k_{eff} (F/k + F/k) = k_{eff} (2F/k)$$ $$1 = k_{eff} (2/k) \implies k_{eff} = \frac{k}{2}$$The frequency of a mass-spring system is given by $f = \frac{1}{2\pi} \sqrt{\frac{k_{eff}}{m}}$. Substituting the expression for $k_{eff}$:
$$f = \frac{1}{2\pi} \sqrt{\frac{k/2}{m}} = \frac{1}{2\pi} \sqrt{\frac{k}{2m}}$$